Counterdependency is a psychological term that describes a person’s aversion to trust and reliance on others, feeling exposed and unhappy when depending on anybody for anything. This behavior is often linked to an avoidant attachment style, where individuals consciously avoid forming attachments or connections with others. By refusing to rely on others, counter-dependent individuals may…
Music Helps Shape Memory Structure Through Emotional Dynamics
Time is a continuous stream, yet our memories are split into discrete episodes, each of which becomes a part of our own narrative. The role of emotions in memory formation is a puzzle that science has only lately begun to explore. UCLA scientists have now shown that the shifting emotions evoked by music aid in…
Relatedness in Self-Determination Theory
The organismic dialectical perspective is a key component within Self-Determination Theory (SDT). This perspective emphasizes the integral relationship between individuals and their social environment, particularly in terms of psychological needs, such as competence, autonomy, and relatedness. At the core of the organismic dialectical perspective lies the concept of basic psychological needs. These needs are viewed as universal and…
Cerebellar Nuclei Has Unexpected Role in Associative Learning
You’ll wait a little longer before drinking from a steaming teacup. And if your fingers get caught in the door, you’ll be more cautious the following time. These are forms of associative learning, where a positive or negative experience leads to learning behavior. We know that our cerebellum is important in this form of learning. But how…
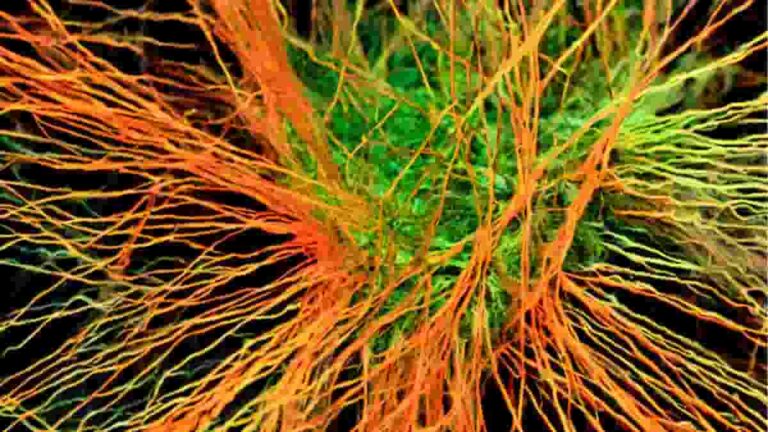
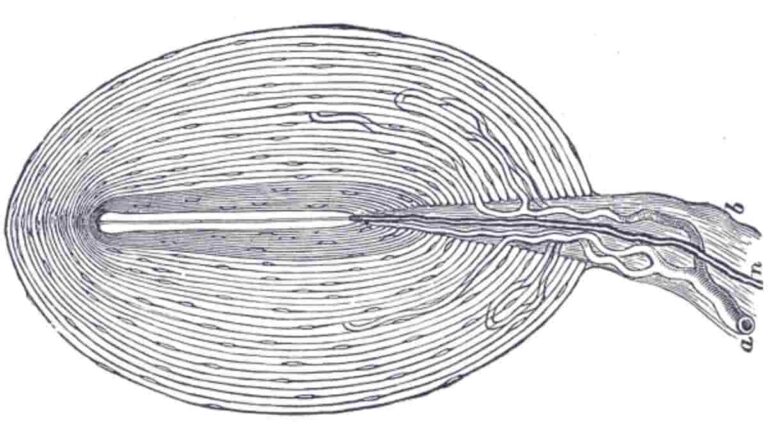
Function of the Pacinian Corpuscle
The Pacinian corpuscle, also known as the lamellar corpuscle or the Vater-Pacini corpuscle, is one of the four basic types of mechanoreceptors found in mammalian skin. This type of mechanoreceptor is found in both hairy and hairless skin, viscera, joints, and bone periosteum, and is principally responsible for vibration sensitivity. Pacinian corpuscles are fast-adaptable (phasic)…
What is Self-Determination Theory? Examples and Differences
Self-Determination Theory (SDT) is a psychological framework that seeks to understand human motivation. Developed by Edward L. Deci and Richard M. Ryan, it focuses on the concepts of autonomy, competence, and relatedness as essential components for fostering intrinsic motivation. SDT comprises several different mini-theories and perspectives, which together provide a comprehensive understanding of human behavior…
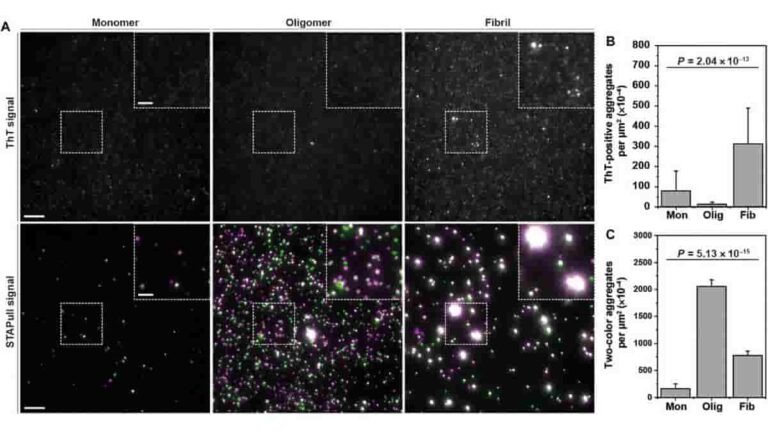
STAPull: Detecting Neurodegenerative Disease Protein Biomarkers
The University of Edinburgh’s Horrocks group has developed a novel solution known as “single-molecule two-color aggregate pull-down,” or STAPull for short, in partnership with UCB Biopharma. Aggregation — a process in which proteins misfold and group together — is a prominent characteristic of a number of neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. These…
Adolescent Brain Biomarkers May Predict Future Psychological Issues
Researchers describe new methods for precisely locating potential biomarkers in teenage brains that are capable of accurately forecasting cognitive growth and mental health problems. Their new study is the first large-scale analysis of its kind, in which researchers analyzed functional network connectivity (FNC) across scans and identified associations with a variety of health measures in…
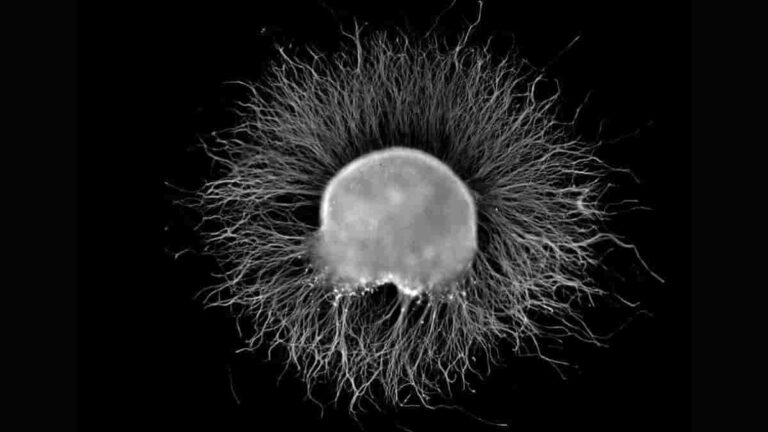
What is the Dorsal Root Ganglion
A dorsal root ganglion, sometimes known as a posterior root ganglion or spinal ganglion, is a group of neurons (a ganglion) in a spinal nerve’s dorsal root. The dorsal spinal nerve root is one of two “roots” that arise from the spinal cord. The dorsal root ganglia contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons known…