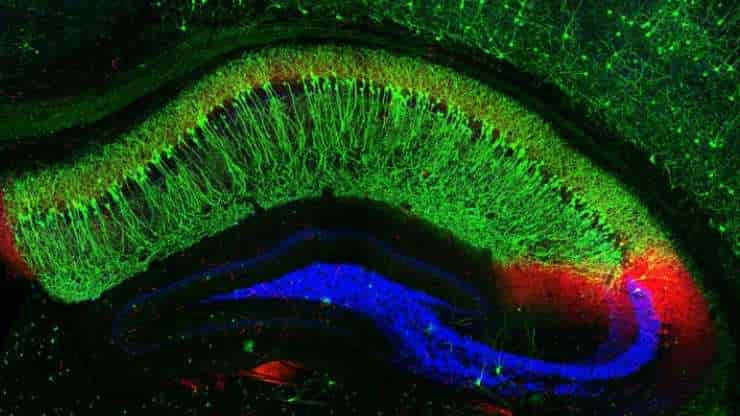
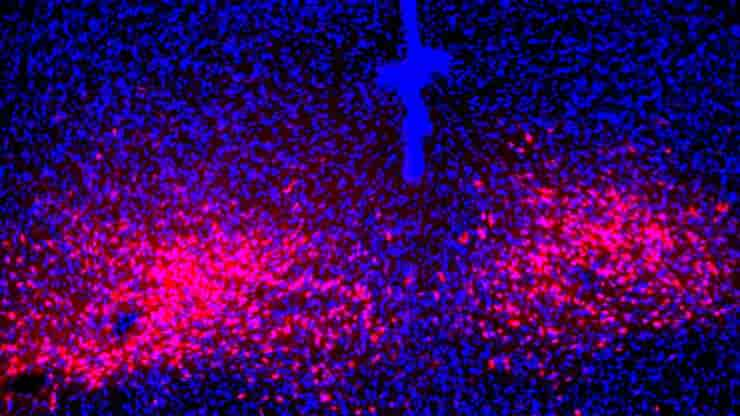
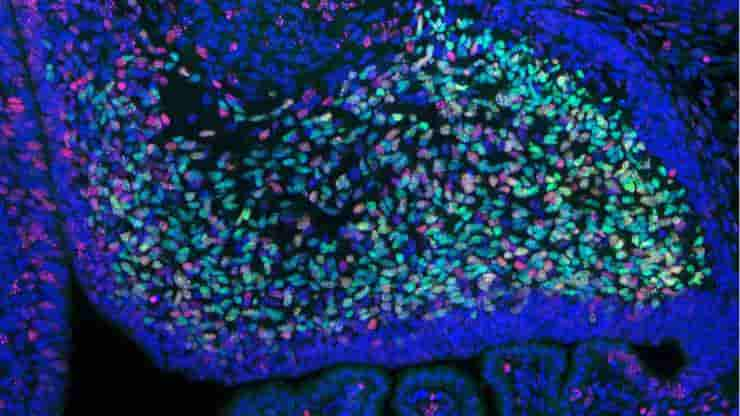
Afferent and efferent neurons are the two primary types of neurons that play distinct yet interconnected roles in this communication network. Afferent nerve fibers, also known as sensory neurons, carry signals from sensory receptors towards the central nervous system. They inform the brain about what is happening in the internal and external environments, thus allowing…
Category: Neuroscience
New Drug Molecule Inhibits Stress Hormone Receptor Activity
Stress is not just an oppressive feeling encountered when one is overburdened; rather, it constitutes the body’s inherent response to acute or persistent strain. The stress response is responsible for facilitating prompt adaptation to peril or changes in circumstances. However, should this physiological reaction — vital for survival — escalate and persist indefinitely, it can…
Superior Colliculus More Important for Vision Than Previously Thought
Researchers at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience discovered that the superior colliculus, a brain area preserved through evolution, is more important for vision than previously thought. Upon visual inspection, an object can be readily differentiated from the surrounding context. Despite the apparent simplicity of this, the manner in which our brain achieves it remains quite…
Substantia Nigra Dopaminergic Activity Regulated by the Cerebellum
Recent research has illuminated a mysterious connection between the brain’s reward center, the basal ganglia, which plays a crucial role in habit formation, and the cerebellum, an anatomically separate area that houses almost three-quarters of the brain’s neurons and aids in motor learning. In addition to potentially altering our basic understanding of how the brain…
Internal Compass Cells May Be Related to Episodic Memory
Since their discovery in the 1990s, the brain’s head-direction cells have been dubbed its “internal compass.” These cells are assumed to be vital for spatial orientation and navigation since they are triggered when an animal’s or human’s head points in a specific direction. A team of neuroscientists from the University of Tübingen has now revealed…
What is the Visual Word Form Area
The visual word form area (VWFA) is a functional region of the left fusiform gyrus and surrounding cortex (the right-hand side is part of the fusiform face area) that is thought to be involved in identifying words and letters from lower-level shape images prior to association with phonology or semantics. Because the alphabet is a…
Key Brain Pathway Affecting Panic Disorder Symptoms Identified
Shortness of breath, sweaty palms, overwhelming fear, rapid heart rate — these are the symptoms of a panic attack, which people with panic disorder have frequently and unexpectedly. Making a map of the brain areas, neurons, and connections that mediate these panic attacks could help in the development of more effective panic disorder treatments. Researchers…
Cerebellum Organoid with Functioning Purkinje Cells Created
A novel human brain organoid model has been developed by the laboratory of Giorgia Quadrato, which is an unprecedented achievement for stem cell scientists at the University of Southern California. The model produces every major cell type of the cerebellum, a region in the hindbrain primarily composed of granule cells and Purkinje neurons—cell types essential…
Retinotopic Coding Transfers Information from Perception to Memory
Humans have vivid memories: we can recall the layout of our house, the color of our bedroom, or the front of our favorite restaurant. Neuroscientists have long been perplexed by how the brain encodes this information. In a recent Dartmouth-led study, researchers uncovered a neural coding process that permits information to be transferred from perceptual…