Researchers have located a neural circuit within the brain that, when activated, generates a profound sensation of discomfort. Additionally, this discovery enables them to demonstrate for the first time that the subthalamic nucleus, a cerebral structure responsible for regulating voluntary movements, might potentially contribute to the pathogenesis of depression. The results could lead to better…
Category: Neuroscience
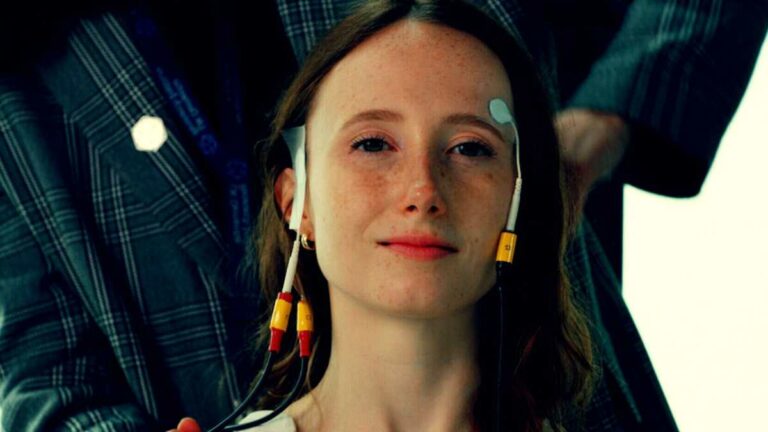
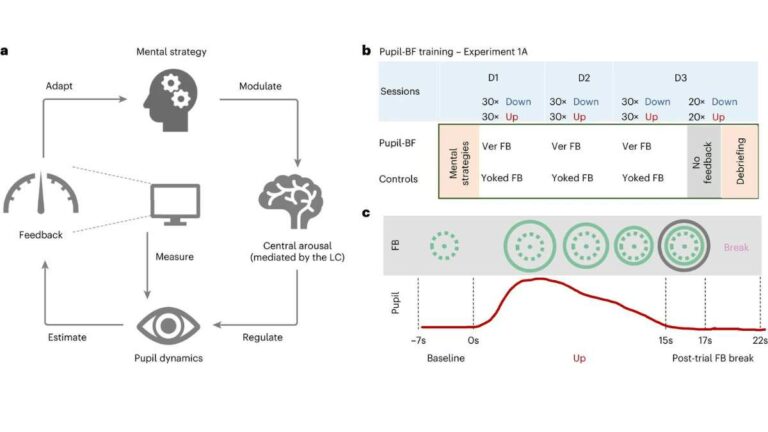
Pupil-based Biofeedback Helps Lessen Anxiety and Stress
Our pupils reflect our level of arousal: they dilate when we are tense, stressed, or even panicked, and constrict when we relax. A nucleus in the pons of the brainstem known as locus coeruleus, which measures roughly 15 millimeters, is crucial to this. It governs our level of arousal via the neurotransmitter noradrenaline and is…
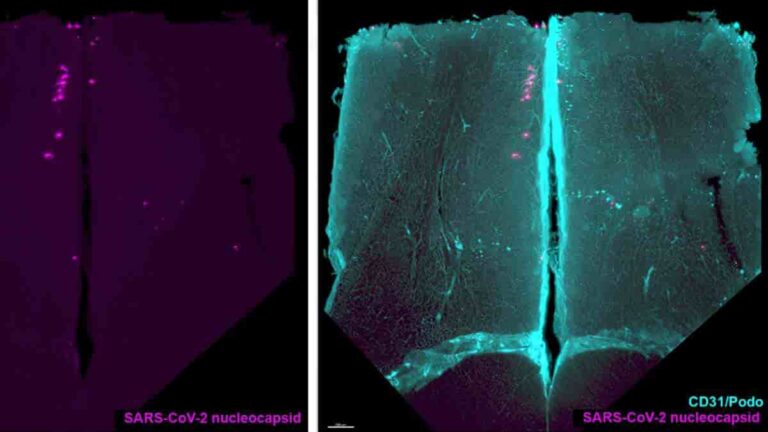
SARS-CoV-2 Virus Spreads Within Neurons
A new study confirms that SARS-CoV-2 is capable of infecting human neurons in vitro and migrating into axons, the nerve cell projections that carry information. The emergence of many SARS-CoV-2 mutations has resulted in a wide range of clinical profiles and symptoms in patients. For the first time, scientists at the Institut Pasteur and Université…
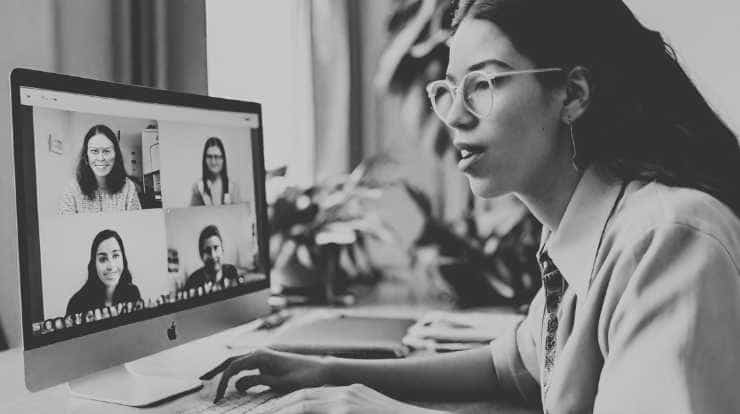
Social Neural Signaling Suppressed During Zoom Conversations
When Yale neuroscientist Joy Hirsch utilized sophisticated imaging technologies to watch the brain activity of two people conversing in real time, she uncovered a complicated choreography of neural activity in parts of the brain that govern social relationships. When she conducted comparable trials with two people communicating on Zoom, the ubiquitous video conferencing platform, she…
Two Brain Regions Key to Semantic Integration While Reading
Two distinct brain regions are essential for integrating semantic information while reading, recent research from the University of Texas Health at Houston suggests. The finding may help explain why people with aphasia struggle with semantics. Language relies heavily on the incorporation of vocabulary across multiple words in order to derive semantic concepts, such as truth…
Investigating the Neural Basis of Concept Formation with Brain-constrained Networks
The impact of language on human thought may be greater than previously believed. This is the conclusion of a recent research conducted by Professor Friedemann Pulvermüller and his team at the Brain Language Laboratory of the Free University of Berlin. Children can acquire multiple languages with minimal effort. However, the cognitive effort required should not…
Strong Signal Changes in Brain’s White Matter Recorded
Researchers from Vanderbilt University report that when people having their brains scanned by fMRI perform a task, such as wiggling their fingers, blood oxygenation-level dependent (BOLD) signals increase in white matter throughout the brain. “We don’t know what this means. We just know that something is happening. There truly is a powerful signal in the…
Temporal Interference Brain Stimulation Promising for Dementia Treatment
Researchers at Imperial College London are leading the development and testing of a novel brain stimulation technique that may offer an alternative therapy for diseases of the brain like Alzheimer’s and the memory loss that goes along with it. The non-invasive technique, known as temporal interference (TI), delivers electrical fields to the brain via electrodes…
Decision-making Brain Areas Have Altered Activity In Teens With OCD
According to a new study from UNSW Sydney, teenagers with obsessive-compulsive disorder have difficulties in decision-making and behavioural control. This is connected to aberrant activity in the orbitofrontal cortex brain region. “OCD is highly prevalent, affecting more than 750,000 Australians. People with OCD get stuck in loops of unwanted thoughts and behaviours,” said first author…