Framing effect bias occurs when the framing of information, whether about gains or losses, alters an individual’s perception and subsequent choices. This cognitive bias is a persuasive force in decision-making, along with other heuristics and psychological biases. It demonstrates that the same information can lead to different conclusions depending on how it is presented. For example, a 75% success rate…
Autonoetic Consciousness
The human ability to mentally place oneself in the past and future (i.e., mental time travel) or in counterfactual scenarios (i.e., alternative outcomes) and so scrutinize one’s own ideas is referred to as autonoetic consciousness. Furthermore, autonoetic consciousness includes behaviors such as mental time travel, self-projection, and episodic future thinking, all of which have been…
Iconic Memory
Iconic memory is a fast-decaying storage of visual information and the visual sensory memory register belonging to the visual domain. It’s part of the visual memory system, together with visual short-term memory (VSTM) and long-term memory (LTM). It supports VSTM by delivering a cohesive representation of our full visual sense for a very short time.…
Baddeley’s Model of Working Memory
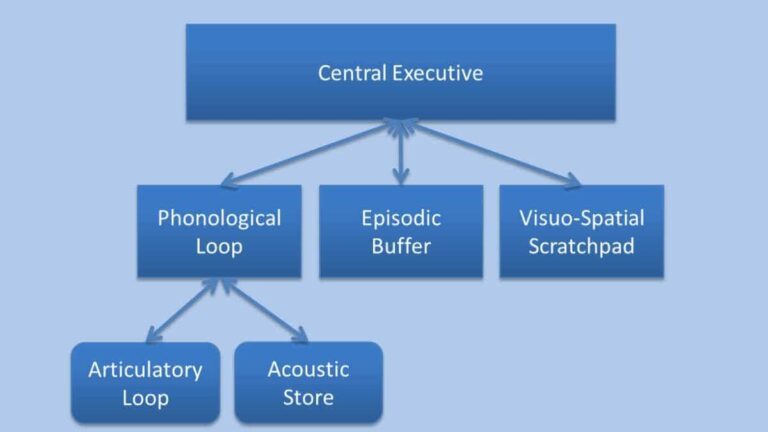
Alan Baddeley and Graham Hitch presented the Baddeley model of working memory in 1974 in an attempt to give a more accurate model of primary memory (also known as short-term memory). Working memory divides main memory into several components rather than viewing it as a unitary construct. As an alternative to the short-term store in…
Neurotypical vs Neurodivergent: the Spectrum of Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity is a term that reflects the diversity of human neurocognitive functioning. It posits that neurological differences such as autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and others are the result of normal, natural variation in the human genome. This framework was first introduced by sociologist Judy Singer in the 1990s, challenging the prevailing view that these neurocognitive variations are inherently…
What is Echoic Memory
Echoic memory is a sensory memory that stores auditory information (sounds). After hearing an auditory stimuli, it is stored in memory so that it can be processed and interpreted. Unlike most visual memories, where a person may choose how long to observe a stimulus and reassess it multiple times, aural stimuli are usually ephemeral and…
Daydreaming May Play a Role in Brain Plasticity
You’re sitting calmly when your mind abruptly tunes out the world and drifts to someplace altogether different – possibly a recent experience or an old recollection. You were having a daydream, as almost everyone does. However, despite the widespread occurrence of this experience, neuroscientists are largely at a loss as to what exactly goes on…
Encoding Memory Types
Memory is capable of encoding, storing, and recalling information, enabling an organism to learn and adapt from prior experiences, as well as to form relationships with other memories. Encoding a memory converts a perceived item of use or interest into a construct that may be stored within the brain and later recalled from long-term memory.…
What Is the Introspection Illusion
Introspection illusion is a term in psychology that denotes a disparity in self-assessment versus assessment of others. People often assume they understand their own motives and preferences distinctly through conscious introspection, yet this introspection does not necessarily provide accurate self-knowledge. This illusion leads them to overestimate their own insights while underestimating those of others, often…