In a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman School of Medicine found that a “chaperone” molecule that inhibits the production of specific proteins reversed disease signs, including memory impairment. The researchers investigated the effects of 4-phenylbutyrate (PBA), a fatty acid molecule known to act as a “chemical chaperone” that…
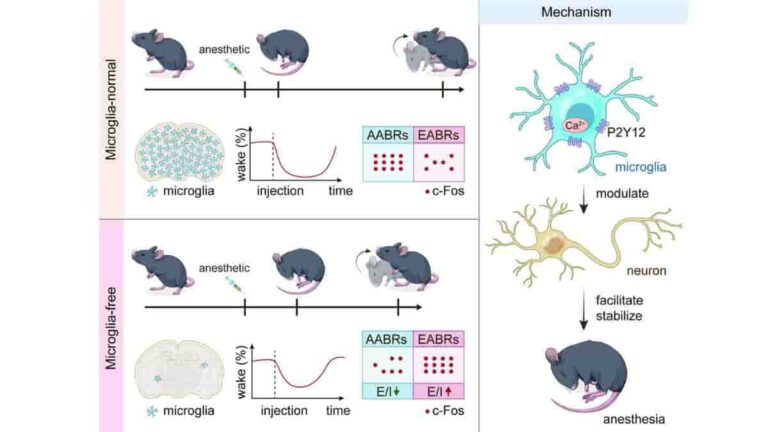
Microglia Aid General Anesthesia by Modulating Regional Neuron Networks
Though it may come as a surprise to the millions of people who have general anesthesia for medical operations each year, the molecular process by which different anesthetics inhibit awareness is still unknown. Researchers may be one step closer after discovering how general anesthesia affects microscopic immune cells in the brain known as microglia. “We…
Apophenia: Finding Patterns in Random Data
Apophenia is a psychological phenomenon in which individuals perceive meaningful patterns or connections within unrelated data. The term was first coined by German psychiatrist Klaus Conrad in his 1958 publication, as a way to describe this tendency to see significance in meaningless randomness. Apophenia has been considered a cognitive error arising from the brain’s need to…
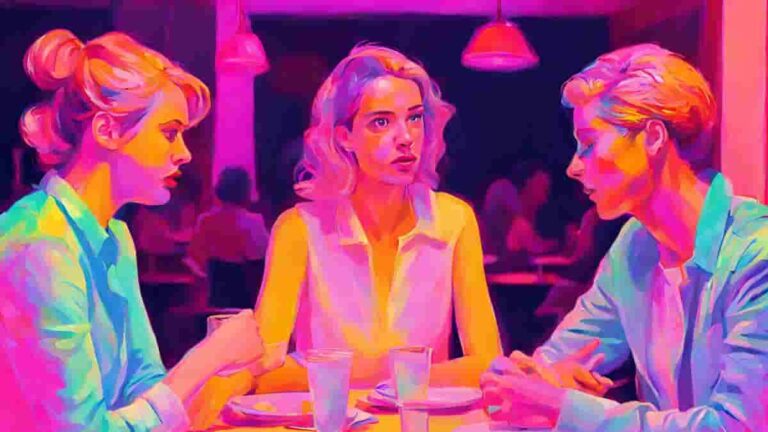
Family Caregiving May Lead to Lower Risk of Depression
Being a caregiver to an aging parent or spouse can be stressful, but a new study calls into question the notion that it is a risk factor for depression. The study found that depression in adult caregivers is mostly driven by having a loved one experiencing serious health problems, while becoming a caregiver is associated…
The Illusory Superiority Cognitive Bias
Illusory superiority is a cognitive bias where individuals tend to overestimate their own qualities and abilities relative to others. This phenomenon is sometimes referred to as the superiority bias. People affected by illusory superiority tend to believe they are better than average in various aspects of life, such as intelligence, skill, or moral values. Some…
Brain Activity Pattern Serves as Experiential Sequence Template
Norwegian University of Science and Technology researchers have discovered a pattern of brain activity that can be used to build sequential experiences. The finding of a rigid sequence pattern in the brain provides new insights into how we organize experiences into a temporal order. “I believe we have found one of the brain’s prototypes for…
False-Uniqueness Effect: the Illusion of Specialness
The false-uniqueness effect is a well-studied phenomenon in social psychology that deals with an individual’s tendency to perceive their own abilities or personal attributes as more unique than they actually are. This cognitive bias leads people to overestimate their distinctiveness in comparison to others, especially regarding positive traits or desirable behaviors. Various studies have demonstrated…
Understanding the False Consensus Effect
The false consensus effect is a well-known cognitive bias in social psychology, where individuals tend to overestimate the extent to which their opinions, beliefs, and behaviors are shared by others. It is categorized as an egocentric bias because it results from people’s tendency to project their own beliefs onto others. One of the factors contributing to the…
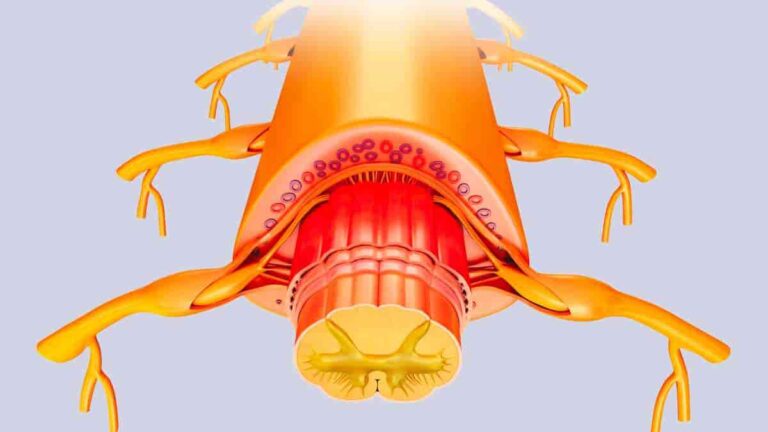
Spinal Cord Stimulation Shows Promise for Depression Treatment
Electrical stimulation of the spinal cord is feasible, well-tolerated, and has therapeutic potential for treating depression, according to a pilot clinical trial led by University of Cincinnati researchers at the Lindner Center of HOPE.The research of principal investigator Francisco Romo-Nava, MD, Ph.D., focuses on how the brain-body connection is involved in psychiatric disorders. “We think…