Psychologists complete an extensive academic program, typically earning a doctoral degree in psychology (Ph.D. or Psy.D.), which includes research and clinical practice. Psychiatrists are medical doctors, meaning they have attended medical school and obtained an M.D. or D.O., and their training strongly focuses on psychiatry as a major component of medicine. Psychiatrists’ training qualifies them…
Category: Psychiatry
Monoamine Hypothesis of Depression
Scientific studies have shown that different brain areas exhibit altered activity in humans suffering from major depressive disorder (MDD), which has encouraged supporters of various theories that try to find a biochemical origin for the disease, as opposed to theories that emphasize psychological or situational causes. One of these theories is the monoamine hypothesis, which…
Bullied Teenagers’ Brains Show Chemical Changes Linked To Psychosis
Teens who are bullied by their peers are more likely to experience early psychotic episodes, which is linked to decreased levels of a critical neurotransmitter in the area of the brain responsible for controlling emotions, according to new research. This research implies that a particular neurotransmitter might be a good candidate for pharmaceutical treatments meant…
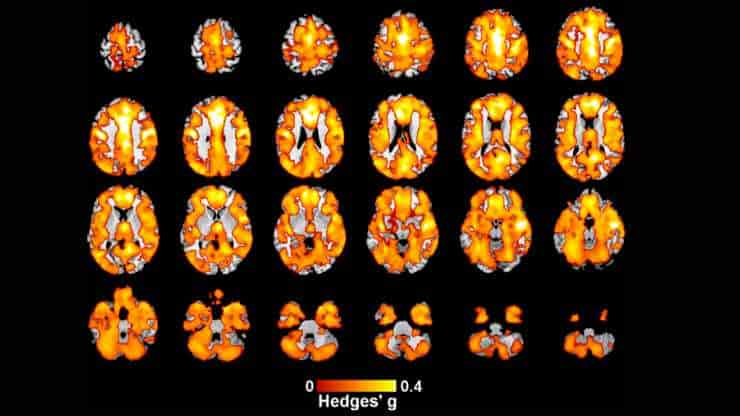
Early Onset Psychosis Linked With Reduced Brain Gray Matter
A new study from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, and Neuroscience has discovered a link between a decrease in gray matter in the brain and early onset psychosis (EOP). The research, the largest brain imaging study ever conducted in EOP, offers unparalleled amounts of data regarding the illness. It demonstrates that, in comparison to other…
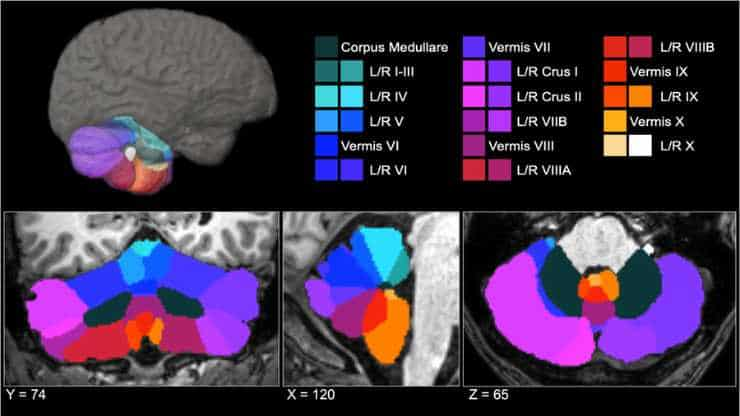
Smaller Cerebellums Observed in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
According to new research from a Duke-led brain imaging study, adults with PTSD have smaller cerebellums. The cerebellum, a region of the brain known for dealing with movement and balance, can influence mood and memory, both of which are affected by posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). What is unknown is whether a smaller cerebellum predisposes a…
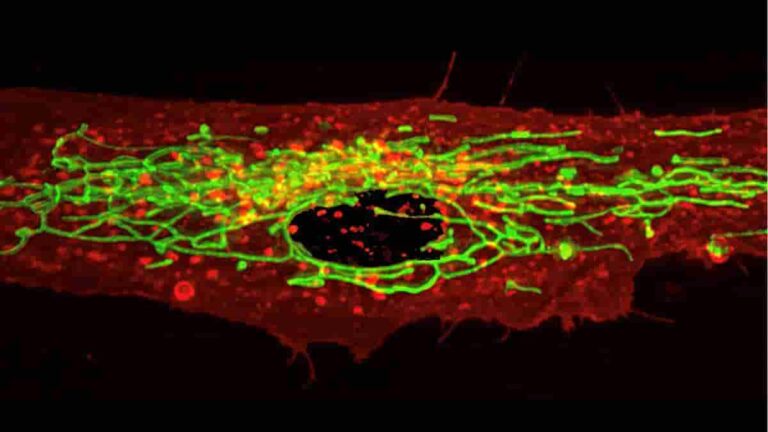
Somatostatin Neurons Growth Hormone Activity Helps Regulate Anxiety
Growth hormone (GH) operates on various tissues throughout the body, including the bones and muscles. It is also an effective anxiolytic. Researchers from the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil recently conducted a study that deepened our understanding of the role of growth hormone in reducing anxiety and, for the first time, identified the…
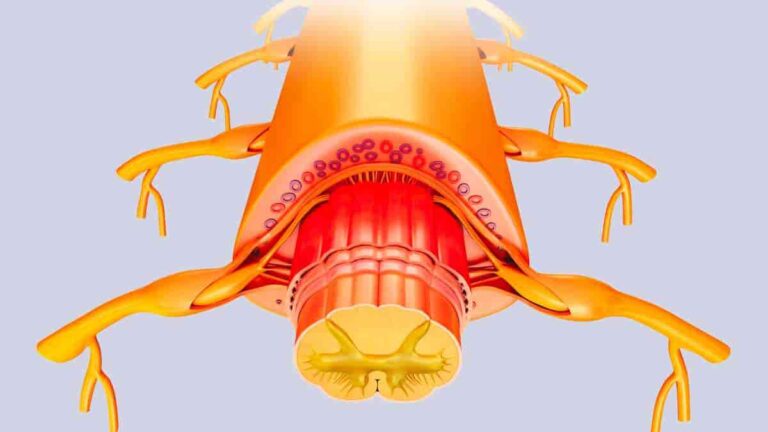
Spinal Cord Stimulation Shows Promise for Depression Treatment
Electrical stimulation of the spinal cord is feasible, well-tolerated, and has therapeutic potential for treating depression, according to a pilot clinical trial led by University of Cincinnati researchers at the Lindner Center of HOPE.The research of principal investigator Francisco Romo-Nava, MD, Ph.D., focuses on how the brain-body connection is involved in psychiatric disorders. “We think…
Cannabis-related Psychiatric Disorders Are On the Rise
The increased potency and pervasive use of cannabis (marijuana) are associated with an increase in cannabis-related psychiatric disorders, according to a new review article published in the New England Journal of Medicine by the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM). It emphasizes the critical necessity for physicians to promptly identify and manage patients exhibiting…
Blood Test Detects Suicidal Ideation Biomarkers
In the United States alone, 16.1 million adults suffer from major depression, which costs $210 billion each year. While the major symptoms of depression are psychological in nature, scientists and clinicians have come to realize that depression is a complicated disease with physical consequences throughout the body. Measuring markers of cellular metabolism, for example, has…