A team of University of Pittsburgh mathematicians is using computational models to better understand how the structure of neural variability relates to such functions as short-term memory and decision making. The team examined how fluctuations in brain activity can impact the dynamics of cognitive tasks. Previous recordings of neural activity during simple cognitive tasks show…
Category: Neuroscience
What Is The Limbic System
The limbic system is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the cerebrum. It has also been referred to as the paleomammalian cortex. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. The limbic system supports a variety of functions…
The Brain Mechanism That Controls Reward Enjoyment
What characterizes many people with depression, schizophrenia and some other mental illnesses is anhedonia: an inability to gain pleasure from normally pleasurable experiences. Exactly why this happens is unclear. But new research led by neuroscientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine may have literally shined a light on the…
What Is Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging?
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) is a functional neuroimaging procedure using MRI technology that measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that…
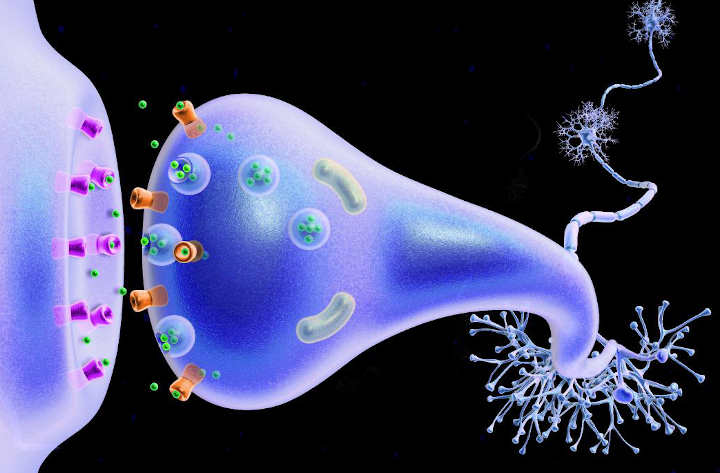
What is a Synapse?
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell (neural or otherwise). Santiago Ramón y Cajal proposed that neurons are not continuous throughout the body, yet still communicate with each other, an idea known as the neuron doctrine.…
Chronic Stuttering In Adults Linked With Corpus Callosum Differences
Abnormal brain function is a basic feature of speech production tasks for adults who stutter, new research is suggesting. Previously, researchers have suspected that anatomical differences in areas of the brain involved in speech production play a critical role in stuttering. Anatomical differences in the hemispheres of the brain between adults who stutter (AWS) and…
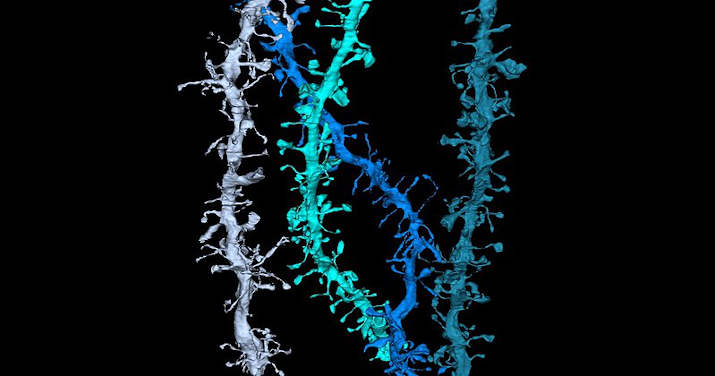
What Are Dendrites?
Dendrites are the branched projections of a neuron that act to propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which they project. Electrical stimulation is transmitted onto them by upstream neurons (usually their axons) via synapses which are located at various points throughout the…
What Is The Caudate Nucleus?
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the dorsal striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia. It plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including procedural learning, and inhibitory control of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose…
What Causes MRI Vertigo? Magnetic Fields to Blame
Researchers from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine says they have discovered why so many people undergoing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), especially in newer high-strength machines, get vertigo, or the dizzy sensation of free-falling, while inside or when coming out of the tunnel-like machine. In the study, a team led by Johns Hopkins scientists suggests…