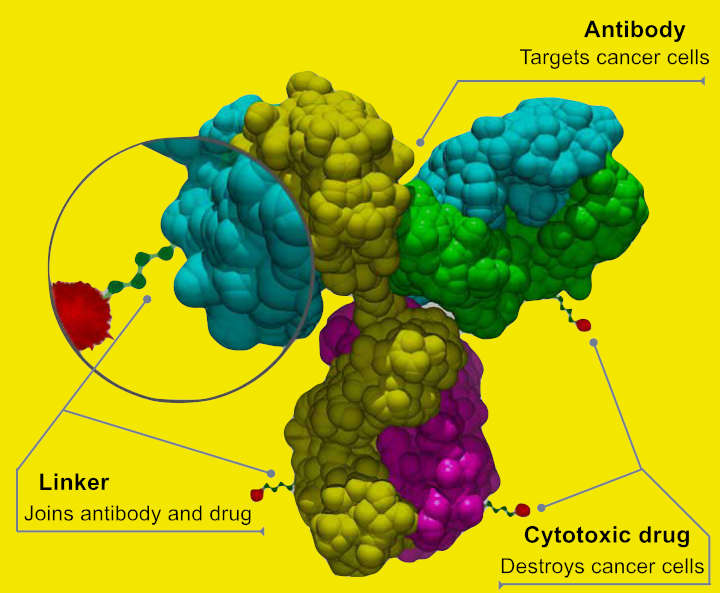
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are a class of biopharmaceutical drugs designed as a targeted therapy for treating cancer. Unlike chemotherapy, ADCs are intended to target and kill tumor cells while sparing healthy cells. As of 2019, some 56 pharmaceutical companies were developing ADCs. Antibody-drug conjugates are complex molecules composed of an antibody linked to a biologically…
Category: Medicine
What Is Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin?
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (brand name Mylotarg), is an antibody-drug conjugate used to treat acute myeloid leukemia. Gemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody to CD33 linked to a cytotoxic agent from the class of calicheamicins. CD33 is expressed in most leukemic blast cells but also in normal hematopoietic cells, the intensity diminishing with maturation of stem cells. Mylotarg…
MAIT Cell Response May Explain Women’s Lower Severe COVID-19 Rate
Women suffer severe COVID-19 at around half the rate as men, but the reason for this has been unclear. Now, research1 has found that women have different levels of mucosal-associated invariant T cells, and these immune cells amass in the lungs, poised to attack the COVID virus. Better armed with these specialized immune cells, women…
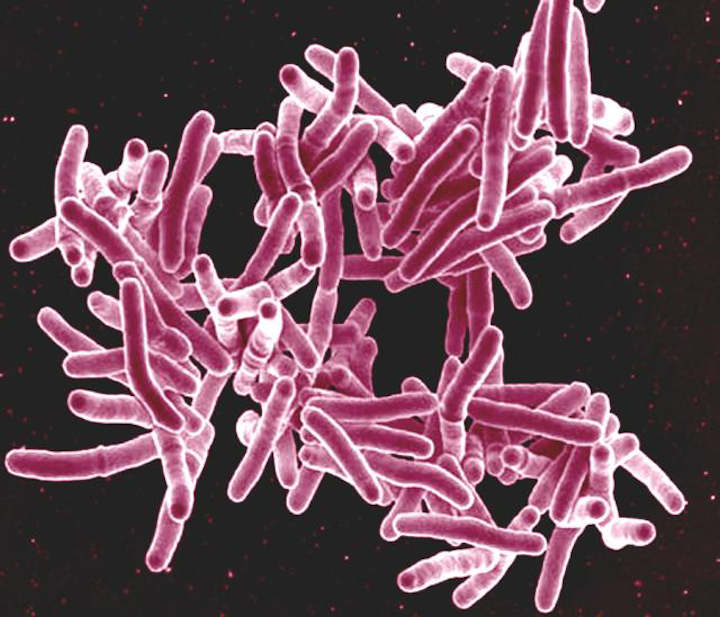
Tuberculosis Bacteria Releases Its Toxin Via Unique Protein Transport System
Two small proteins made by the M. tuberculosis bacteria mediate secretion of it’s toxin by pore formation in the membranes that envelop the bacteria, new research1 shows. Six years ago, Michael Niederweis, Ph.D., described the first toxin ever found for the deadly pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The toxin, tuberculosis necrotizing toxin, or TNT, became the founding…
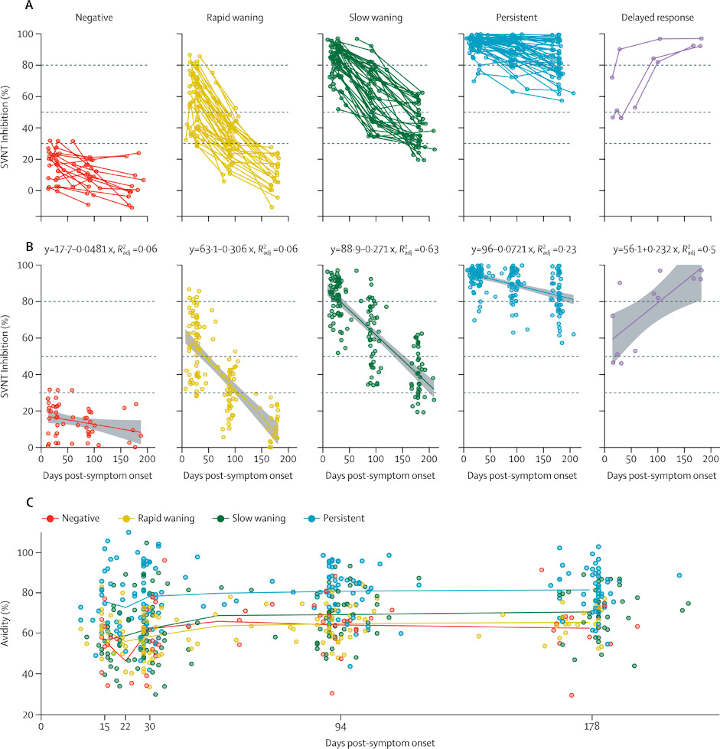
Sars-Cov-2 Antibody Longevity Varies Greatly among Individuals
Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 wane at different rates, lasting for days in some people, while remaining in others for decades, according to machine learning prediction research. A new study1 shows that the severity of the infection could be a deciding factor in having longer-lasting antibodies. People with low levels of neutralizing antibodies may still be protected…
Effects of Quicker Biological Aging Show Up By Middle Age
For people whose bodies age more quickly than others, the cumulative effects show up as early as midlife, when signs of dementia and physical frailty begin to emerge, a study led by Duke researchers found. The results of the study1 suggests that identifying and treating the diseases of old age should begin by the time…
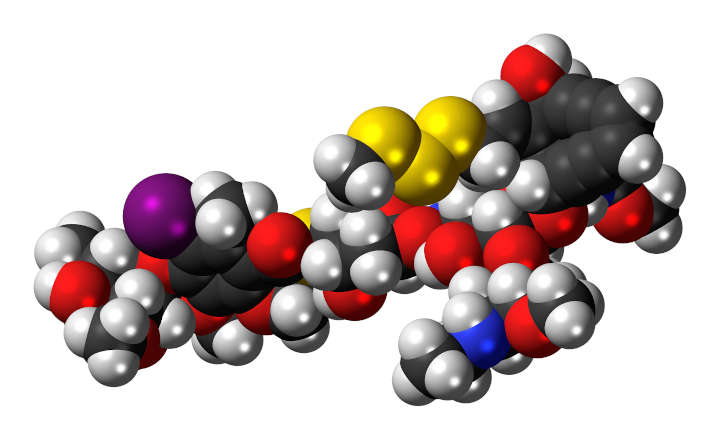
What Is Calicheamicin?
The calicheamicins are a class of enediyne antitumor antibiotics derived from the bacterium Micromonospora echinospora, with calicheamicin γ1 being the most notable. It was isolated originally in the mid-1980s from the chalky soil, or “caliche pits”, located in Kerrville, Texas. The sample was collected by a scientist employed by Lederle Labs (now part of Pfizer)…
Toddlers With Erratic Sleep Patterns Have Higher Body Mass Index
New research from University of Delaware links inconsistent sleep times to higher body mass index (BMI) percentiles. The findings suggest sleep may help explain the association between household poverty and BMI. We’ve known for a while that physical activity and diet quality are very strong predictors of weight and BMI. I think it’s really highlighting…
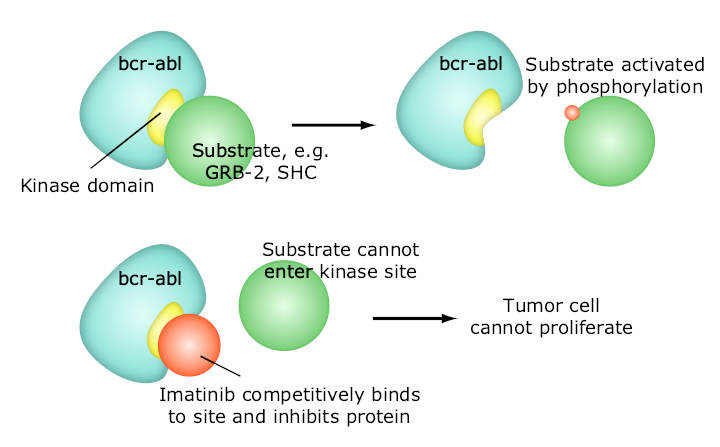
What Is Molecularly Targeted Therapy?
Molecularly targeted therapy, or targeted therapy, is one of the major modalities of medical treatment for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering…