Rutgers researchers argue that facts matter and explain why beliefs are more reasonable than they appear, even when politics and science are at odds with the truth, conspiracy theories are on the rise, and disinformation is widespread. In the study, researchers analyzed previous research and developed a new scientific framework that, according to the researchers,…
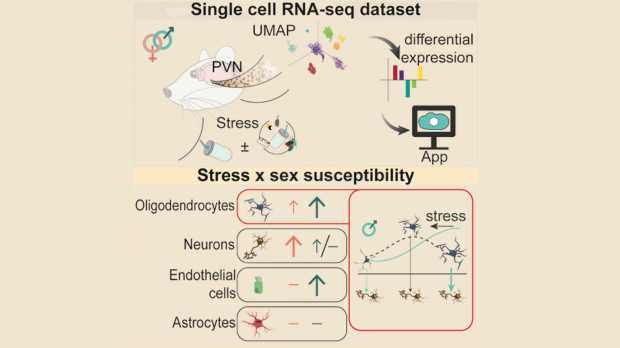
Female and Male Brain Cells Respond Differently to Chronic Stress
Researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science have discovered in unprecedented detail how the brains of male and female mice react differently to stress. The findings may lead to a better understanding of health conditions affected by chronic stress, such as anxiety, depression, and even obesity and diabetes, and pave the way for personalized treatments…
Synaptic Vesicle Dysfunction Triggers Parkinson’s Neurodegeneration
Degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons is widely regarded as the initial cause of Parkinson’s disease. But a new study from Northwestern Medicine researchers challenges the belief. The new research suggests that synaptic dysfunction in neurons precedes neurodegeneration by causing dopamine deficits. “Based on these findings, we hypothesize that targeting dysfunctional synapses before the neurons are degenerated…
The Illusory Truth Effect – Misinformation and Cognition
The Illusory Truth Effect is a cognitive bias in which people tend to believe that a statement is true if they have encountered it before. The phenomenon happens whether the interval between repetitions is minutes, weeks, or even months. Furthermore, the effect is independent of the source of the remarks and occurs even when participants…
What is Repetition Priming
Repetition priming is the enhancement of a behavioural response when stimuli are given repeatedly. Accuracy or reaction time improvements might occur when the repeated stimuli are either the same or similar to the preceding stimuli. It has been demonstrated that these improvements are cumulative, so that as the number of repetitions increases, responses become progressively…
What is Implicit Memory? Implicit vs Explicit Memories
Implicit memory, also known as unconscious or automatic memory, refers to the unconscious form of memory that influences our thoughts and behaviours without conscious awareness. It encompasses all the information acquired and stored in the brain, which enables us to carry out various tasks such as riding a bike, typing on a keyboard, and even…
Why Do You Get Anxiety Over a Messy House?
Do you ever feel overwhelmed by the sight of clutter and mess in your home? Have you walked in the door only to feel overloaded by scattered papers, unwashed dishes and clothes in disarray? Maybe you’ve even had arguments because it bothers you more than it bothers you partner or housemates. You’re not alone. Many…
NPTX2 Protein Predicts Cognitive Impairment Years In Advance
A protein found in the spinal fluid of cognitively healthy adults predicted the onset of mild cognitive impairment and dementia years before symptoms appeared, a new study has found. The findings could lead to new targets for treating or preventing Alzheimer’s and other dementias. Combined with last week’s news of a previously unknown path of…
What is Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation, also known as emotional self-regulation, refers to an individual’s ability to manage, respond to, and modify their own emotional experiences. This process helps in maintaining a balanced and healthy emotional state, promoting positive interpersonal interactions, reducing the impact of negative emotions on the individual’s mental health, and maximizing positive emotional experiences. Developing effective…