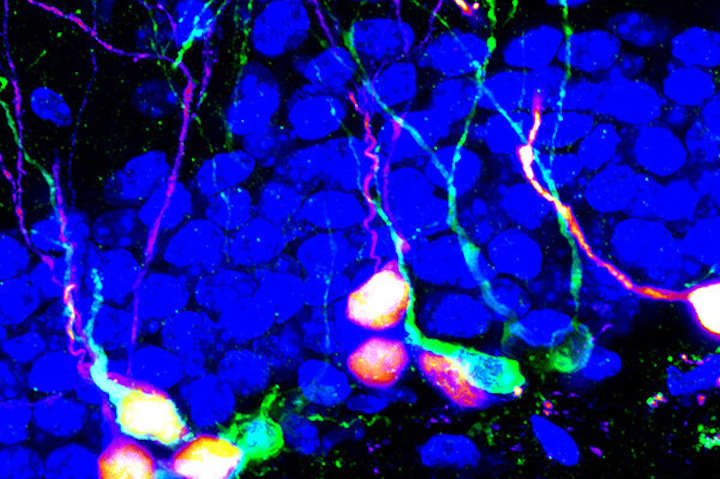
Researchers at University of North Carolina School of Medicine have zeroed in on a specific kind of neuron in mice to increase the production of neural stem cells and spur on the creation of new adult neurons. Targeting these cells modulated memory retrieval and altered anxiety-like behaviors in mice, their study1 details.
Targeting the hypothalamic neurons to enhance adult hippocampal neurogenesis will not only benefit brain functions, but also holds the potential to treat cognitive and affective deficits associated with various brain disorders,
said senior author Juan Song, Ph.D.
Adult Neurogenesis
Most neurons in our brains were created before we were born and are organized during early childhood. But such neurogenesis continues into adulthood and throughout life. In fact, one of the reasons for cognitive decline and anxiety, and even diseases such as Alzheimer’s, is the suspension of neurogenesis.
We know that adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus plays a critical role in memory and emotion processing, and that neural circuit activity regulates this process in a constantly changing manner. But whether this neural circuit activity could be manipulated to spur neurogenesis to such a degree that the effect would be seen as a changed behavior, such as better memory or less anxiety remained unknown.
To observe the effect of modulating neural activity, the researchers used optogenetics to trigger neuronal activity in a small brain structure called the supramammillary nucleus (SuM). The SuM is located inside the hypothalamus region of the brain; it helps manage things from cognition to locomotion and sleep/wakefulness.
Increased Neural Stem Cells
When Song’s researchers chronically stimulated the SuM neurons, they discovered a robust promotion of neurogenesis at multiple stages. They observed increased production of neural stem cells and the creation of new adult-born neurons with enhanced properties.
Optogenetic stimulation of these new neurons then altered memory and anxiety-like behaviors.
We also show that the SuM neurons are highly responsive when the mice experienced new things in their environment. In fact, in a new environment, mice require these cells for neurogenesis,
Song said.
Impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis correlates with many pathological states, such as aging, neurodegenerative diseases, and mental disorders. So targeting the hypothalamic neurons to enhance adult hippocampal neurogenesis should not only benefit brain functions but also hold possibilities of treating cognitive and affective deficits associated with various brain disorders.
- Li, YD., Luo, YJ., Chen, ZK. et al. Hypothalamic modulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice confers activity-dependent regulation of memory and anxiety-like behavior Nat Neurosci 25, 630–645 (2022). ↩︎
Last Updated on October 14, 2022