Proprioception, also referred to as kinaesthesia, is the sense of self-movement and body position.[1] It is sometimes described as the sixth sense. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, mechanosensory neurons located within muscles, tendons, and joints. There are multiple types of proprioceptors which are activated during distinct behaviors and encode distinct types of information: limb velocity…
Category: Resources
What Is A Virus?
It may seem like a fairly fundamental question, but there is still debate over whether viruses should be considered a form of life. The diversity of viral infections is immense. Viruses cause everything from common cold (rhinoviruses) to Ebola and warts (papillomavirus); from HIV/AIDS to influenza and smallpox. Many viruses can cause cancer: the hepatitis…
Microglia Definition
Microglia, also known as Microgliocytes, Gitter cells, or Hortega Cells, are a type of glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for 10–15% of all cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous…
What Is The Precuneus?
The precuneus is a part of the superior parietal lobule in front of the occipital lobe (cuneus). It is hidden in the medial longitudinal fissure between the two cerebral hemispheres. It is sometimes described as the medial area of the superior parietal cortex. The precuneus is bounded anteriorly by the marginal branch of the cingulate…
What Is The Putamen?
The putamen is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain. The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that comprise the basal nuclei. Through various pathways, the putamen is connected to the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, the claustrum, and the thalamus, in…
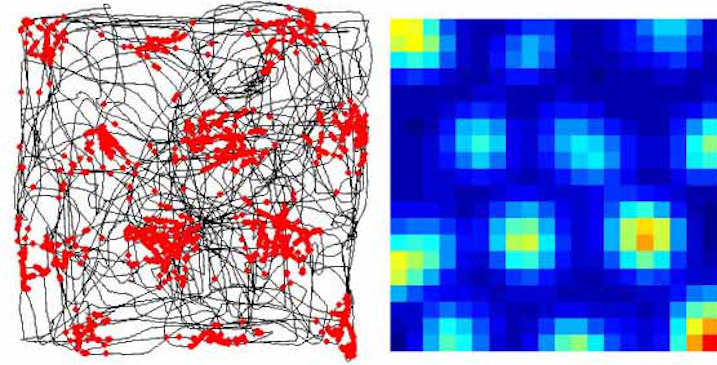
What Are Grid Cells?
A grid cell is a place-modulated neuron whose multiple firing locations define a periodic triangular array covering the entire available surface of an open two-dimensional environment. Grid cells are thought to form an essential part of the brain’s coordinate system for metric navigation. They have attracted attention because the crystal-like structure underlying their firing fields…
What Is The Insular Cortex?
The insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus, the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes. The insulae are believed to be involved in consciousness and play a role in diverse functions usually linked to emotion or the regulation of the body’s homeostasis.…
What Is The Entorhinal Cortex?
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain located in the medial temporal lobe and functioning as a hub in a widespread network for memory and navigation. The EC is the main interface between the hippocampus and neocortex. The EC-hippocampus system plays an important role in declarative (autobiographical/episodic/semantic) memories and in particular spatial…
What Is Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture (the relative amounts of such components can also be determined). In…