The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-shaped brain structure which comprises the lower section of the brainstem. It is in front of and partly under the cerebellum. The cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor nerve centers are contained in the medulla. Consequently, it handles the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood…
Category: Neurology
Having Bad Dreams Could Be Early Parkinson’s Disease Sign
In a group of older men, individuals having frequent bad dreams were twice as likely to be later diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease as those who did not, new research from University of Birmingham reports. Although it can be really beneficial to diagnose Parkinson’s disease early, there are very few risk indicators and many of these…
Anti-inflammatory Exercise Factors That Are Transferrable Benefit the Brain
Blood taken from young adult mice that get lots of exercise benefits the brains of same-aged, sedentary mice, new research1 shows. A single protein called clusterin in the blood of exercising mice seems mainly responsible for the effect. The finding could open the door to treatments that lower risk of neurodegenerative disease or slow its…
What Are Ranvier Nodes
Nodes of Ranvier are myelin sheath gaps. They appear along a myelinated axon where the axolemma is exposed to the extracellular space. Nodes of Ranvier are uninsulated and highly enriched in ion channels, allowing them to participate in the exchange of ions required to regenerate the action potential. Nerve conduction in myelinated axons is referred…
Music’s Potential As A Treatment For Parkinson’s, Stroke, And Brain Injury
You probably don’t realise it when you’re listening to your favourite song, but music has an incredibly powerful effect on the human brain. Singing, playing an instrument or listening to music have all been shown to activate numerous areas of the brain that control speech, movement and cognition, memory and emotion – often all at…
Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Elevate Following Major Cardiac Surgery
Blood levels of a substance proven to be highly predictive of the onset of Alzheimer’s disease rose markedly during cardiac surgery and remained elevated for two days post-surgery, which was when levels were last measured, a small study has found. Heart surgery, a lengthy operation typically involving substantial tissue injury, is particularly stressful and causes…
T-cell Response Worsens Neurodegeneration In Lewy Body Dementias
CD4+ T cells respond to buildups of alpha-synuclein, a Northwestern Medicine study has found. Alpha-synuclein are a feature of neurodegenerative diseases including dementia with Lewy bodies (LWD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD). This autoimmune response proves harmful, and inhibiting signaling pathways that trigger the response may represent a future therapeutic target, according to David Gate, Ph.D.,…
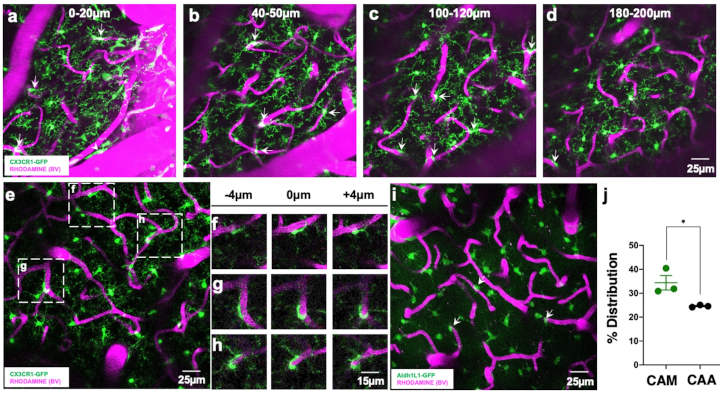
Microglia Help Regulate Blood Flow In The Brain
Microglia help regulate blood flow and maintain the brain’s critical blood vessels, University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have found. It is an important but previously unknown role for these immune cells that protect the brain from disease and injury. The findings1 may prove important in cognitive decline, dementia and stroke, among other conditions…
Modified Macrophage Metabolism Aids Peripheral Nerve Regeneration
Macrophages can be altered to support and speed the regeneration of peripheral nerves in mice following injury, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have found. The nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, known as peripheral nerves, have the capacity for regeneration, but the rate of natural renewal is so slow that many nerve injuries lead to…