Associative inference occurs when the brain’s retrieval of certain memories is hindered by the presence of similar associations. This is particularly observable in associative learning settings, where memories are connected through learned associations. For instance, learning new information can interfere with the retrieval of older, related information, a phenomenon known as retroactive interference. Conversely, prior learning can disrupt…
Tag: memory
Proactive vs Retroactive Interference in Memory
Interference refers to a phenomenon in cognitive psychology where competing information can hinder the storage and retrieval of memories. It is commonly segmented into two types: proactive interference and retroactive interference. Proactive interference arises when older memories disrupt the recall of new information. Conversely, retroactive interference occurs when new information causes difficulties in retrieving older memories. Both types of interference can affect long-term…
Imagination Inflation: Memory’s Creative Expansion
Imagination inflation occurs when individuals develop greater confidence in the truth of an event after imagining it, potentially leading to the formation of false memories. The term often relates to childhood memories, as these are typically more malleable and susceptible to misconceptions. Several factors have been linked to an increase in the imagination inflation effect. Imagining a fictitious…
What is State-Dependent Memory: Context in Recall
State-dependent memory refers to when a person’s ability to recall information is influenced by their particular mental or physical state state at the time of encoding the memory. If the internal state during recall matches the state during encoding, retrieval of the memory is typically more successful. This cognitive psychology concept highlights the tight interplay…
The Atkinson-Shiffrin Model of Memory: Multi-store Memory
The Atkinson-Shiffrin model of memory, formulated by psychologists Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin, offers a structured illustration of the human information processing system. First proposed in 1968, the model includes three main components: Sensory memory: A temporary repository that captures all sensory information, where most of it is lost unless attention is directed to it. Short-term store:…
Semantic Memory
Semantic memory refers to long-term memory that processes ideas and concepts that are not drawn from personal experience; our autobiographical memory. This type of memory includes common knowledge, such as the fact that Paris is the capital of France or that a dog is an animal, rather than recalling a specific event or occurrence. It is a part…
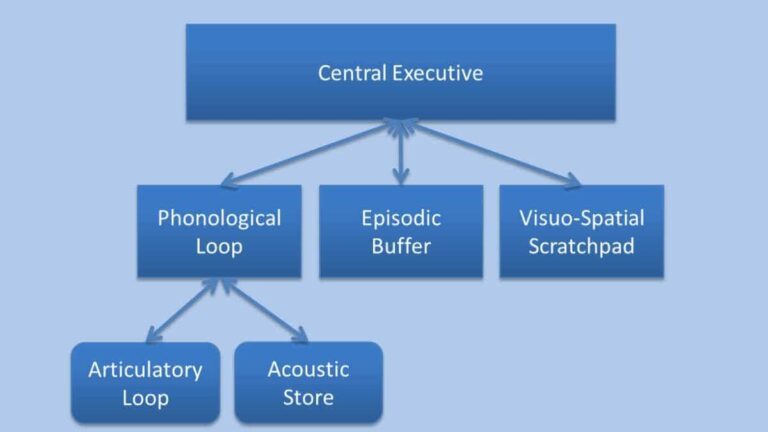
Baddeley’s Model of Working Memory
Alan Baddeley and Graham Hitch presented the Baddeley model of working memory in 1974 in an attempt to give a more accurate model of primary memory (also known as short-term memory). Working memory divides main memory into several components rather than viewing it as a unitary construct. As an alternative to the short-term store in…
Encoding Memory Types
Memory is capable of encoding, storing, and recalling information, enabling an organism to learn and adapt from prior experiences, as well as to form relationships with other memories. Encoding a memory converts a perceived item of use or interest into a construct that may be stored within the brain and later recalled from long-term memory.…
Long Term Potentiation
Long-term potentiation (LTP), in neuroscience, refers to a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are synaptic activity patterns that result in a long-term increase in signal transmission between two neurons. Long-term depression, the inverse of LTP, results in a long-term decline in synaptic strength. It is one of several mechanisms…