Amyloid protein produced in the liver can cause neurodegeneration in brain tissue, a new study1 by John Mamo of Curtin University, and colleagues has found. Since the protein is thought to be a key contributor to development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the results suggest that the liver may play an important role in the onset or progression of the disease.
Deposits of amyloid beta (A-beta) in the brain are one of the pathological hallmarks of AD and are implicated in neurodegeneration in both human patients and animal models of the disease.
But A-beta is also present in periphereral organs, and blood levels of A-beta correlate with cerebral amyloid burden and cognitive decline, raising the possibility that peripherally produced a-beta may contribute to the disease.
Testing that hypothesis has been difficult, since the brain also produces amyloid beta, and distinguishing protein from the two sources is challenging.
Liver Expression Of Amyloid
The study’s authors overcame that challenge by developing a mouse that produces human amyloid beta only in liver cells. They showed that the protein was carried in the blood by triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, just as it is in humans, and passed from the periphery into the brain.
They found that mice developed neurodegeneration and brain atrophy, which was accompanied by neurovascular inflammation and dysfunction of cerebral capillaries, both commonly observed with Alzheimer’s disease. Affected mice performed poorly on a learning test that depends on function of the hippocampus, the brain structure that is essential for the formation of new memories.
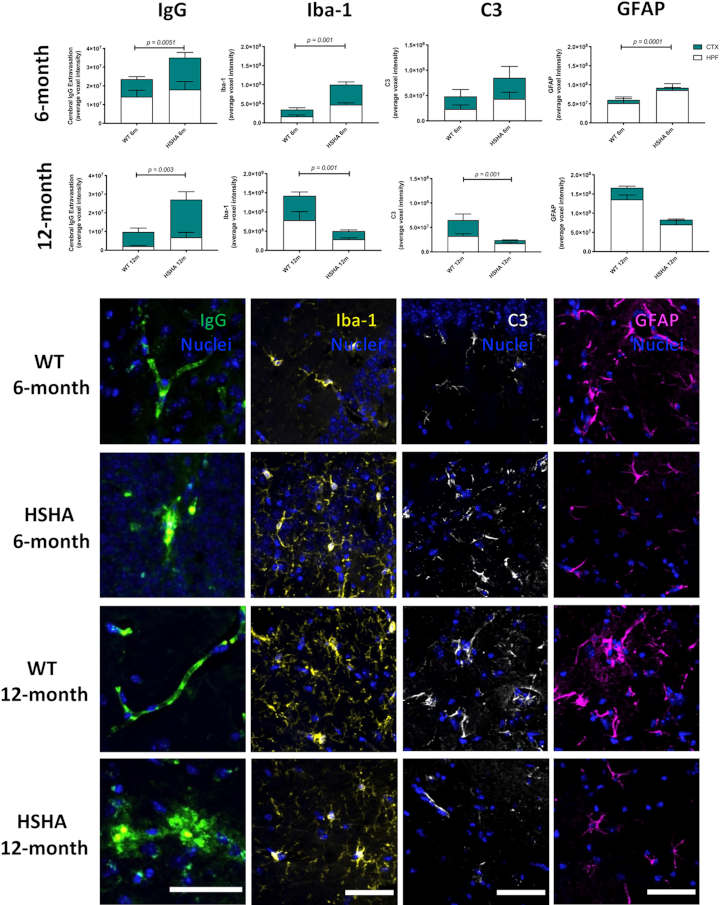
The hepatocyte-specific human amyloid (HSHA) strain of mice represent a novel opportunity to specifically investigate the triglyceride-rich lipoprotein to amyloid beta metabolic chain as it relates to neurovascular integrity.
Lifestyle Factors
The findings indicate that peripherally derived A-beta has the ability to cause neurodegeneration and suggest that amyloid beta made in the liver is a potential contributor to human disease. If that contribution is significant, the findings may have major implications for understanding Alzheimer’s disease.
To date, most models of the disease have focused on brain overproduction of A-beta, which mimics the rare genetic cases of human Alzheimer’s. But for the vast majority of AD cases, overproduction of amyloid beta in the brain is not thought to be central to the disease etiology.
Instead, lifestyle factors may play a more important role, including a high-fat diet, which might accelerate liver production of A-beta.
While further studies are now needed, this finding shows the abundance of these toxic protein deposits in the blood could potentially be addressed through a person’s diet and some drugs that could specifically target lipoprotein amyloid, therefore reducing their risk or slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease,
Mamo said.
The work was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council, and by the Western Australian Department of Health.
- Lam V, Takechi R, Hackett MJ, Francis R, Bynevelt M, Celliers LM, et al. Synthesis of human amyloid restricted to liver results in an Alzheimer disease–like neurodegenerative phenotype. PLoS Biol 19(9): e3001358 ↩︎
Last Updated on November 11, 2023