Music can be a drug-free method of reducing our pain perception, according to previous research. This reduced sensitivity to pain, also referred to as hypoalgesia, can occur when there is a pause between the time that pain stimuli are received and the conscious mind recognizes them as pain. A recent study by scientists in Montreal…
Social Neural Signaling Suppressed During Zoom Conversations
When Yale neuroscientist Joy Hirsch utilized sophisticated imaging technologies to watch the brain activity of two people conversing in real time, she uncovered a complicated choreography of neural activity in parts of the brain that govern social relationships. When she conducted comparable trials with two people communicating on Zoom, the ubiquitous video conferencing platform, she…
Mild Cognitive Impairment Undiagnosed In Over 7 Million Americans
For many people, forgetting your keys or having difficulty planning tasks may appear to be a typical part of aging. However, those gaps may be signs of something more serious: mild cognitive impairment, or MCI, which could be an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease. Unfortunately, because most people with MCI are unaware of it, they…
Willful Ignorance Often Comes From Selfishness
A recent study has found that 40% of people will choose ignorance over knowing how their actions will affect others, frequently as a justification for acting selfishly. “Examples of such willful ignorance abound in everyday life, such as when consumers ignore information about the problematic origins of the products they buy,” said lead author Linh…
Two Brain Regions Key to Semantic Integration While Reading
Two distinct brain regions are essential for integrating semantic information while reading, recent research from the University of Texas Health at Houston suggests. The finding may help explain why people with aphasia struggle with semantics. Language relies heavily on the incorporation of vocabulary across multiple words in order to derive semantic concepts, such as truth…
Investigating the Neural Basis of Concept Formation with Brain-constrained Networks
The impact of language on human thought may be greater than previously believed. This is the conclusion of a recent research conducted by Professor Friedemann Pulvermüller and his team at the Brain Language Laboratory of the Free University of Berlin. Children can acquire multiple languages with minimal effort. However, the cognitive effort required should not…
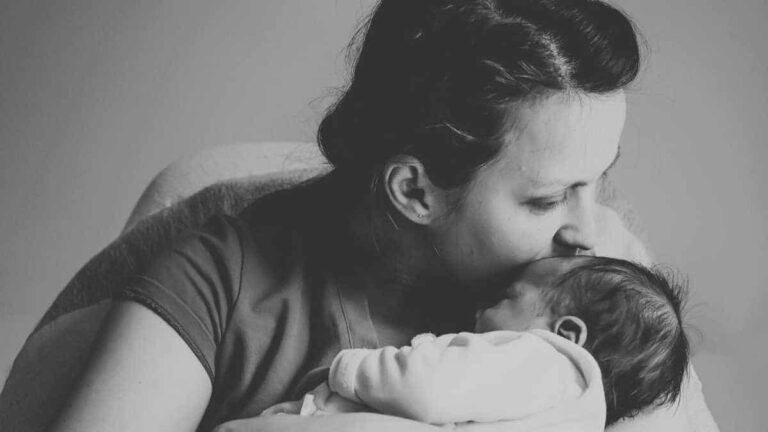
Heritability of Postpartum Depression Confirmed by Researchers
Postpartum depression (PPD), a prevalent subtype of major depressive disorder, is more heritable than other psychiatric conditions, such as anxiety and bipolar disorder, but the genetics of PPD are understudied in comparison. To address this, University of North Carolina School of Medicine researchers led an international team of researchers in the largest-ever meta-analysis of genome-wide…
Insomnia is Linked with Mental Disorders But Exactly How is Still Unknown
The 2004 movie The Machinist gives us a striking depiction, albeit a fictional one, of the psychological effects of chronic insomnia. When people don’t have enough sleep, their memory and concentration are impaired in the short term. They are also less able to regulate their emotions. If sleeping difficulties continue, longer-term psychological effects can include…
Strong Signal Changes in Brain’s White Matter Recorded
Researchers from Vanderbilt University report that when people having their brains scanned by fMRI perform a task, such as wiggling their fingers, blood oxygenation-level dependent (BOLD) signals increase in white matter throughout the brain. “We don’t know what this means. We just know that something is happening. There truly is a powerful signal in the…