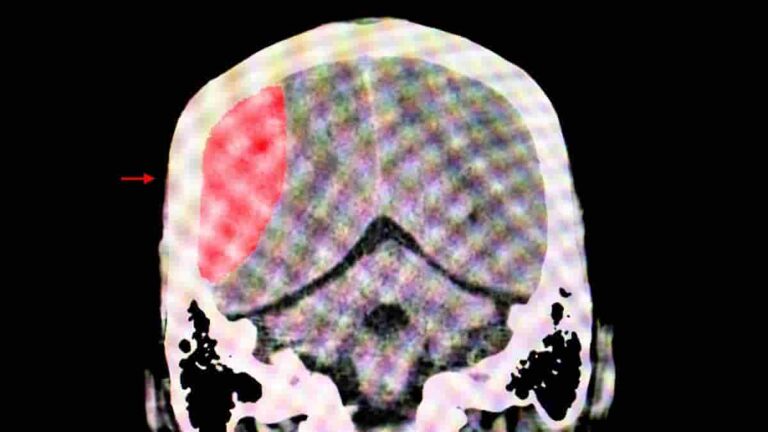
According to new research from the University of British Columbia, a particular type of genetic test that helps determine the best antidepressant for patients with moderate-to-severe depression could generate significant healthcare savings and greatly improve patient outcomes. The study found that pharmacogenomic testing might save the provincial public health system $956 million over the course…
Embodied Learning Improves Children’s Literacy Skills
Children who form letter sounds with their bodies outperform those who learn spelling in a traditional classroom, according to new research. Children who are at risk of having reading difficulties can benefit from the learning strategy just as much as those with normal literacy development. Literacy skills development is a crucial element of a child’s…
More Brain Genes are Altered by Early-life Stress Than by a Head Injury
When researchers began investigating whether early-life stress compounded the consequences of a childhood head injury on health and behavior later in life, they discovered something unexpected. Stress changed the activation level of many more genes in the brain than a head injury did in an animal research model. Head injuries are known to be prevalent…
The Benefits of Keeping Good News to Yourself
Though people often want to share good news as soon as they learn it, a new study has found that keeping good news a secret before telling someone else could make people feel more energized and alive. “Decades of research on secrecy suggest it is bad for our well-being, but this work has only examined…
How Your Brain Assigns Blame for Mistakes
The human mind dislikes making mistakes and works hard to avoid doing them again. A new study from the University of Iowa researchers illustrates how the human brain can discern between outcomes caused by human error and those that are not directly to blame in just one second. Furthermore, the researchers discovered that in cases…
Depersonalization vs. Dissociation Disorder: Key Differences
Depersonalization and dissociation are both complex psychological phenomena, but they manifest differently and involve distinct features. Understanding the key differences between them is important for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Depersonalization is a specific type of dissociative experience characterized by feelings of unreality and detachment from one’s own thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations. People with…
Key to Infantile Amnesia Could Be Autism Brain States
Researchers in the field of neuroscience have found an interesting link between being able to remember things from your childhood and the way brains develop in people with autism. Most of us have little recollection of our lives prior to the age of two. The term infantile amnesia refers to this seeming complete loss of episodic…
How Much of Mindfulness Meditation Research is Pseudoscience?
In 2019, Debra Halsch was diagnosed with smoldering multiple myeloma, a rare blood and bone marrow disorder that can develop into a type of blood cancer. Her doctors recommended chemotherapy, she said, but she feared the taxing side effects the drugs might wreak on her body. Instead, the life coach from Piermont, New York tried…
Temporal Structure of Memory Consolidation Brain Waves Revealed
The reactivation of patterns of neural activity based on experience is critical for learning and memory. Yet, these patterns and the associated brain waves vary greatly and are difficult to categorize. Such events, known as ripples, are typical of the hippocampus, a brain area responsible for remembering. Up until now, frequency analysis has been the…