Semantic memory refers to long-term memory that processes ideas and concepts that are not drawn from personal experience; our autobiographical memory. This type of memory includes common knowledge, such as the fact that Paris is the capital of France or that a dog is an animal, rather than recalling a specific event or occurrence. It is a part…
What is the Visual Word Form Area
The visual word form area (VWFA) is a functional region of the left fusiform gyrus and surrounding cortex (the right-hand side is part of the fusiform face area) that is thought to be involved in identifying words and letters from lower-level shape images prior to association with phonology or semantics. Because the alphabet is a…
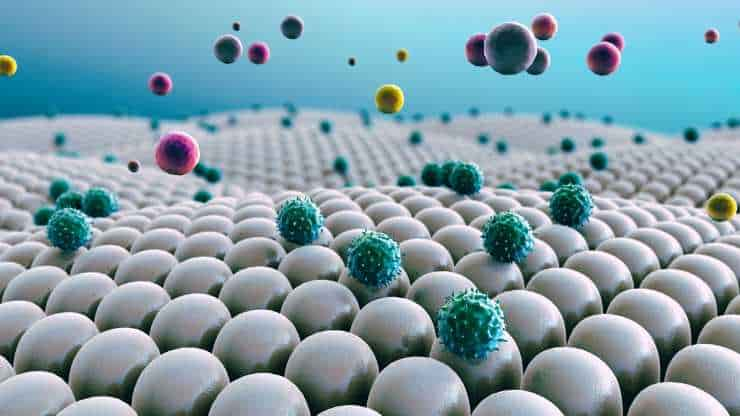
Hydrogel-based Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Diagnosis Technique
Researchers have developed a new brain imaging tool that can detect mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBIs) even when conventional imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) show no structural abnormalities. The method includes injecting gadolinium, a common MRI contrast agent, into hydrogel-based micropatches connected to immune cells known as macrophages. mTBIs generate inflammation in…
How Your Brain Compensates for Multi-tasking
We’re all time-poor, so multi-tasking is seen as a necessity of modern living. We answer work emails while watching TV, make shopping lists in meetings and listen to podcasts when doing the dishes. We attempt to split our attention countless times a day when juggling both mundane and important tasks. But doing two things at…
Functional Fixedness: Breaking Mental Models to Enhance Problem Solving
Functional fixedness is a cognitive bias that limits a person’s ability to use objects only in the way they are traditionally used. Discovered by psychologist Karl Duncker, it represents the mental shortcuts that often prevent individuals from seeing potential innovative uses for common items. Functional fixedness hinders problem-solving because it restricts awareness to an item’s most familiar…
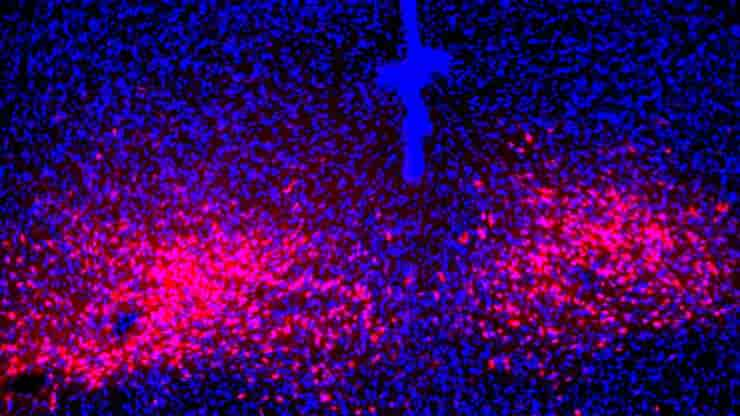
Key Brain Pathway Affecting Panic Disorder Symptoms Identified
Shortness of breath, sweaty palms, overwhelming fear, rapid heart rate — these are the symptoms of a panic attack, which people with panic disorder have frequently and unexpectedly. Making a map of the brain areas, neurons, and connections that mediate these panic attacks could help in the development of more effective panic disorder treatments. Researchers…
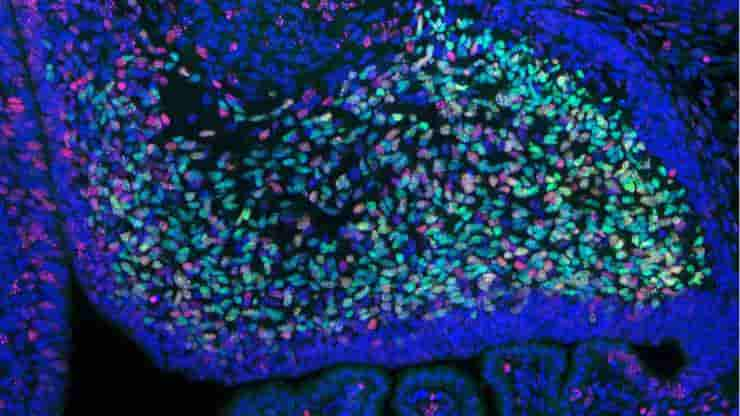
Cerebellum Organoid with Functioning Purkinje Cells Created
A novel human brain organoid model has been developed by the laboratory of Giorgia Quadrato, which is an unprecedented achievement for stem cell scientists at the University of Southern California. The model produces every major cell type of the cerebellum, a region in the hindbrain primarily composed of granule cells and Purkinje neurons—cell types essential…
What Is Depressive Realism and Is It Real?
Depressive realism is a term used to describe the hypothesis that depressed individuals can assess their control, performance, and outcomes in a more accurate manner than those who are not depressed. The phenomenon suggests that, contrary to common beliefs about depression warping reality, these individuals may not overestimate their influence or capabilities, which contributes to a…
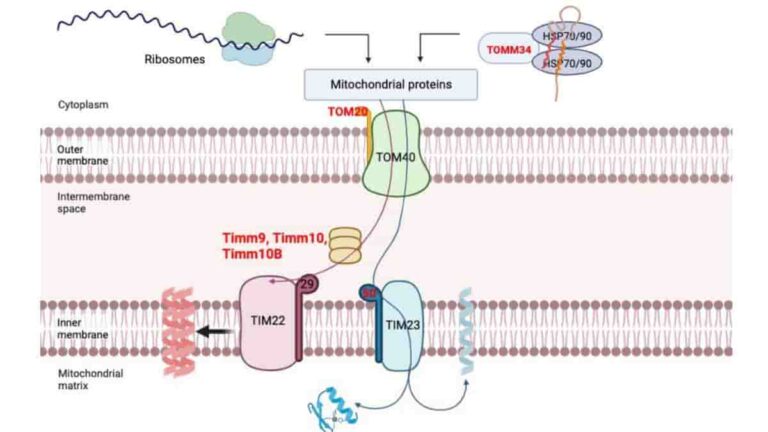
Newly Found Gene Variant a Protective Factor in Parkinson’s Disease
A new study from the University of Southern California Leonard Davis School of Gerontology reveals that a genetic mutation in a small protein, which had not been previously identified, confers substantial protection against Parkinson’s disease and provides a novel avenue for investigating potential treatments. The variation, found in a mitochondrial microprotein called Small Humanin-like Peptide…