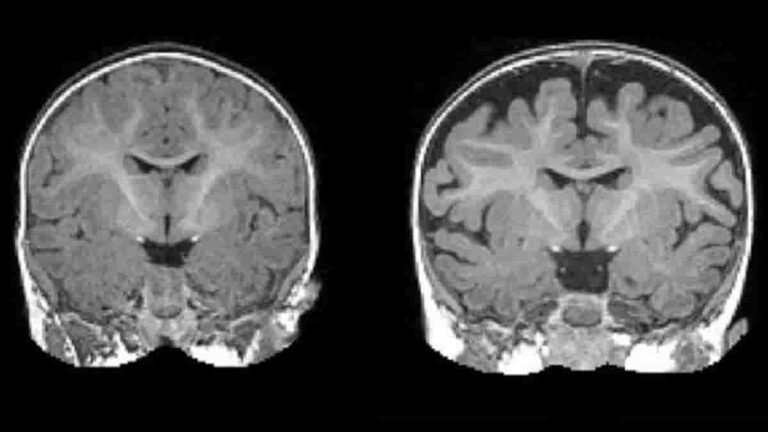
Many toddlers diagnosed with autism at two years of age had a substantially greater amount of extra-axial cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) at six and 12 months of age, before diagnosis is possible, a research network led by UNC School of Medicine’s Joseph Piven, MD has found. They also found that the more CSF at six months…
Category: Neurology
Air Pollution Exposure May Increase Risk Of Dementia
Of the leading causes of death in America, Alzheimer’s disease is the only one that we currently cannot prevent, cure or even stall. Our latest research seeks to change this situation by providing a better understanding of the environmental causes and mechanisms behind the disease. Our findings lead us to conclude that outdoor air pollution,…
Lafora Disease: Potential Third Causitive Factor Identified
In addition to gene mutations, chemical modification of the enzyme Laforin induced by nitrosative stress has been found to be a likely cause of Lafora disease as well, researchers at Okayama University report. Lafora disease is a fatal illness characterized by the abnormal generation of glycogens within neurons and other cells, for which no cure…
Sleeping 9 Hours Or More Linked To Higher Dementia Risk
People that sleep more than nine hours each night consistently had twice the risk of developing dementia in 10 years compared to participants who slept for 9 hours or less, a new study has shown. The study also found those who slept longer had smaller brain volumes. A large group of adults enrolled in the…
Multiple Sclerosis Seizures Linked To Chronic Demyelination
Multiple sclerosis patients are three to six times more likely to develop seizures – abnormal hyperactivity of nerve cells – compared to the rest of the population. But despite increased occurrence of seizures among these patients, little research has been done to probe why they happen. Chronic demyelination is closely linked to, and is likely…
Sugar And Alzheimer’s Disease Molecular Link Revealed
A molecular “tipping point” that could explain sugar’s ties to Alzheimer’s disease has been identified by a group of U.K. researchers. The team has demonstrated that excess glucose damages a vital enzyme involved with inflammation response to the early stages of Alzheimer’s. It is already known that abnormally high blood sugar levels, or hyperglycaemia, is…
Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration Linked to Altered Tau Isoform Ratio
Loss of the interaction between two RNA binding proteins changes the expression ratio of different forms of tau protein, research from a team led by Nagoya University scientists has found. The altered ratio produces the frontotemporal lobar degeneration phenotype in mice, and that this could be rescued by rebalancing the tau ratio. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration…
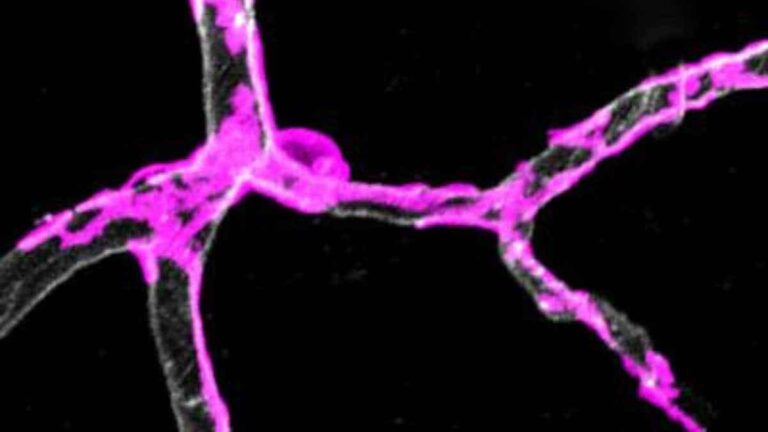
Pericyte Degeneration Limits Brain’s Oxygen Supply
Abnormalities in pericytes, cells that wrap around capillaries in the brain, lead to neuron deterioration, possibly affecting the development of Alzheimer’s disease, a study led by University of Southern California researchers reports. Pericytes are “gatekeeper cells” that surround blood vessels. They contract and dilate to regulate blood flow to active parts of the brain, in…
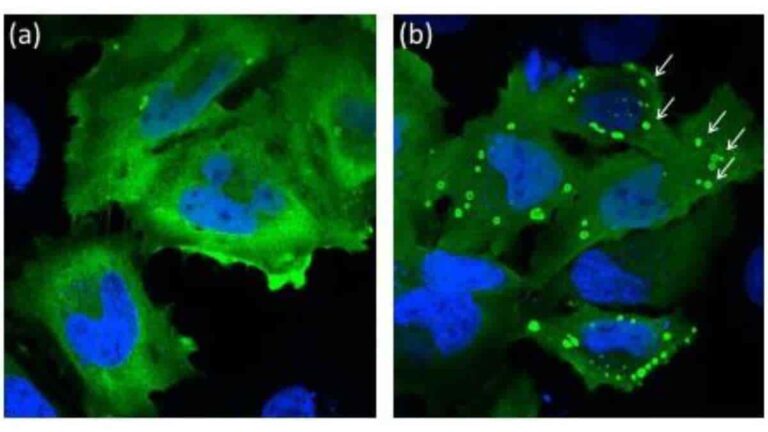
Ubiquitin Proteasome System Faults May Contribute To Parkinson's
A fault with the waste removal system that helps to keep our brain cell mitochondria healthy may play a role in neurodegenerative disease, a new study led by researchers at the University of Nottingham has found. The finding supports previous evidence that patients with Parkinson’s disease have faults with brain mitochondria which contributes to dysfunction…