Young adults’ Adderall misuse and related emergency room trips have risen dramatically even as their prescriptions for the stimulant hold steady, research shows. The study, published online by the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, rebuts the common perception that Adderall misuse is worse among adolescents and older children than among 18-to-25-year-olds. The study examined trends from…
Author: D.C.Demetre
What If We Could Record And Rewind Our Thoughts?
Scientific discoveries that involve humans interfacing with machines can evoke reactions of fear and wonder. Quite often, these feelings are epitomized through works of science fiction. Think Mary Shelly’s “Frankenstein,” for starters; or its modern day equivalent, one of many films playing on our mixed feelings toward AI, “Ex Machina.” One British sci-fi TV series…
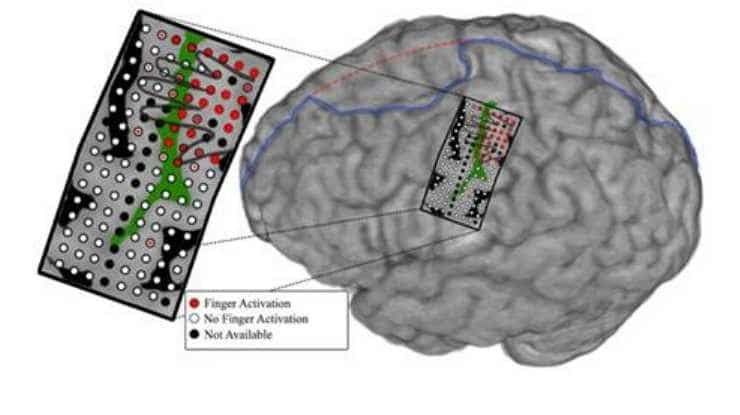
Mind-controlled Prosthetic Arm Moves Individual Fingers
Physicians and biomedical engineers from Johns Hopkins report what they believe is the first successful effort to wiggle fingers individually and independently of each other using a mind-controlled artificial arm to control the movement. The proof-of-concept feat represents a potential advance in technologies to restore refined hand function to those who have lost arms to…
Vulnerability To Depression Linked To Noradrenaline
The team of Bruno Giros, a researcher at the Douglas Mental Health University Institute and professor of psychiatry at McGill University, reports the first-ever connection between noradrenergic neurons and vulnerability to depression. This finding paves the way for new depression treatments that target the adrenergic system. Stressful life events, such as job loss, accident, death…
Sound Symbolism Boosts Learning New Words
What makes some words easier to learn than others? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics and Radboud University taught Japanese words to Dutch students and found that ideophones – words that sound like what they mean – are easier to learn than regular words. This suggests that some of our associations between sound…
Past Pleasures Make It Hard To Say No
Our brains are wired to pay more attention to things that have previously brought us pleasure, a bias that may explain why it’s so hard to break bad habits or stick to New Year’s resolutions. Neuroscientists demonstrated that when people see something associated with a past reward, their brain flushes with the neurotransmitter chemical dopamine,…
Memory Replay Prioritizes High-reward Memories
Why do we remember some events, places and things, but not others? Our brains prioritize rewarding memories over others, and reinforce them by replaying them when we are at rest, according to new research from the University of California, Davis, Center for Neuroscience. Said Professor Charan Ranganath, a UC Davis neuroscientist and senior author on…
Brain Must Regulate Its Neural Networks To Preserve Memories
Memory, i.e. our ability to record, to preserve and to recall our past experiences, makes up one of the most fundamental and fascinating abilities of our brain. For over forty years, neuroscientists have been interested in the biological mechanisms underlying the storage of the information that our brain records every day. Now, a team from…
Key Role Of Nucleocytoplasmic Transport In ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) are two devastating adult-onset neurodegenerative disorders. No cure exists for these diseases. Ten percent of ALS patients suffer from a familial form of the disease, while FTD is caused in 40% of patients by a genetic defect. In 2011, the most important genetic cause of ALS and…