Astrocyte dysfunction is associated with Parkinson’s disease (PD) pathology in new research using induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology. The study, from the University of Eastern Finland, highlights the role of brain astrocyte cells in PD pathology and the potential of iPSC-derived cells in disease modeling and drug discovery.
PD’s exact cause is still unknown, but several molecular mechanisms have been identified in PD pathology. These include neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, dysfunctional protein degradation and alpha-synuclein pathology.
The disease’s major hallmarks include the loss of dopaminergic neurons and the presence of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. The loss of dopaminergic neurons and the subsequent decrease in dopamine levels are considered responsible for PD’s typical movement symptoms.
There is no cure for PD and currently, the treatments are targeted to alleviate the motor symptoms with dopamine replacement therapy and surgery.
Risk Factors
The biggest risk factor for PD is advanced age, but some environmental factors, such as toxins and pesticides, have been shown to increase PD risk. Though most PD cases are late-onset and sporadic with no evidence for an inheritance, approximately 3-5 % are monogenic.
The most common cause for monogenic PD is mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene. LRRK2-associated PD is clinically closest to sporadic forms of the disease regarding the age of onset, disease progression and motor symptoms.
Additionally, mutations in the GBA (glucosylceramidase beta) gene are the most significant risk factor for PD identified to date. The molecular mechanisms by which GBA mutations result in this increased risk are currently the focus of substantial research efforts.
Astrocyte Contribution To PD
While studies focusing on dopaminergic neurons have brought new insight into PD pathology, astrocyte contribution to PD has been investigated only sparsely.
It was long thought that the astrocytes worked solely as supporting cells for neurons, but today the role of astrocytes is known to be far more extensive. Until now, only a few studies have used iPSC-derived astrocytes obtained from PD patients.
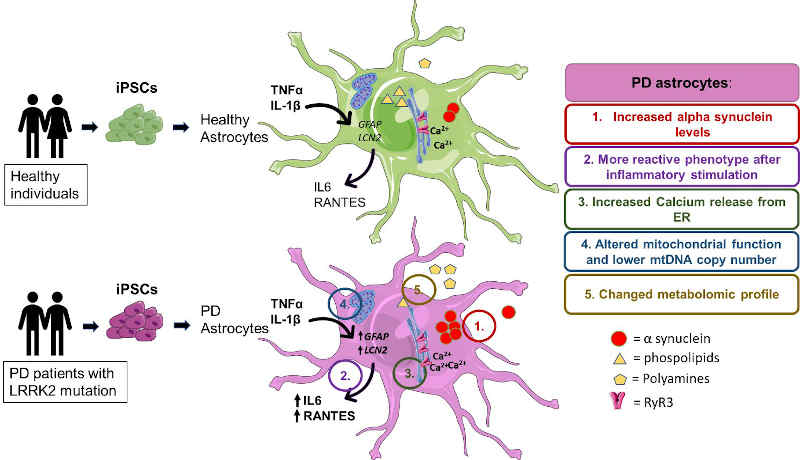
The current study used iPSC-derived astrocytes from two PD patients carrying a mutation in the LRRK2 gene, one of them presenting with an additional mutation in GBA to further characterize the PD astrocyte phenotype.
Alpha-synuclein
The researchers found out that astrocytes from PD patients produced significantly higher levels of α-synuclein, a protein that accumulates in PD patients’ brain. One of the key pathological features caused by α-synuclein aggregation is the disruption of calcium homeostasis, and the study showed increased calciumlevels in PD astrocytes.
As inflammation is considered to be an important contributor to PD pathology, the response to inflammatory stimuli was studied in astrocytes. The PD patient astrocytes were highly responsive to inflammatory stimuli and more sensitive to inflammatory reactivation than control astrocytes.
Additionally, PD astrocytes showed altered mitochondrial function and lower mitochondrial DNA copy number. Furthermore, PD astrocytes showed increased levels of polyamines and polyamine precursors while lysophosphatidylethanolamine levels were decreased, both of these have been reported altered in PD brain.
“The results provide evidence that LRRK2 and GBA mutant astrocytes are likely to contribute to PD progression and offer new perspectives for understanding the roles of astrocytes in the pathogenesis of PD,”
says researcher Tuuli-Maria Sonninen, the lead author of the study.
Image: PD patients’ astrocytes manifest several hallmarks of the disease, these include: (1) increased production of alpha-synuclein, (2) increased reactivity upon inflammatory stimulation, (3) increased astrocytic Ca2+ levels, (4) mtDNA maintenance defects and (5) metabolomic changes. Image credit: Tuuli-Maria Sonninen