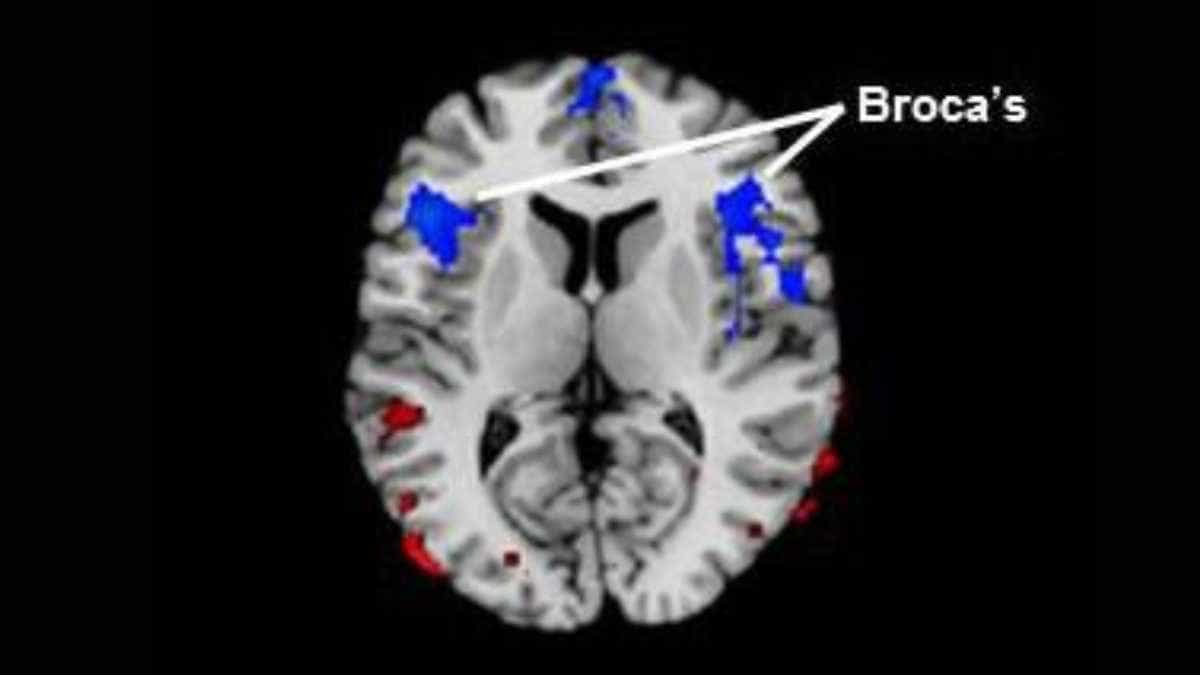
Cerebral blood flow is reduced in Broca’s area, the region in the frontal lobe of the brain linked to speech production, in people who stutter, a study led by researchers at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles has shown. More severe stuttering is associated with even greater reductions in blood flow to this region.
In addition, a greater abnormality of cerebral blood flow in the posterior language loop, associated with processing words that we hear, correlates with more severe stuttering. This finding suggests that a common pathophysiology throughout the neural “language” loop that connects the frontal and posterior temporal lobe likely contributes to stuttering severity.
Lead investigator Bradley Peterson, MD, refers to “a critical mass of evidence” of a common underlying lifelong vulnerability in both children and adults who stutter.
Speech Processing Disturbances
Peterson, who is director of the Institute for the Developing Mind at CHLA and a professor of the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California, says that such a study of resting blood flow, or perfusion, has never before been conducted in persons who stutter.
His team also recently published a study using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy to look at brain regions in both adults and children who stutter.
Those findings demonstrated links between stuttering and changes in the brain circuits that control speech production, as well as those supporting attention and emotion. The present blood flow study adds significantly to the findings from that prior study and furthermore suggests that disturbances in the speech processing areas of the brain are likely of central importance as a cause of stuttering.
According to Peterson, the new study provides scientists with a completely different window into the brain. The researchers were able to zero in on Broca’s area as well as related brain circuitry specifically linked to speech, using regional cerebral blood flow as a measure of brain activity, since blood flow is typically coupled with neural activity.
First author Jay Desai, MD, a clinical neurologist at CHLA, said:
“When other portions of the brain circuit related to speech were also affected according to our blood flow measurements, we saw more severe stuttering in both children and adults. Blood flow was inversely correlated to the degree of stuttering – the more severe the stuttering, the less blood flow to this part of the brain,” said Desai, adding that the study results were “quite striking.”
Reference:
- Jay Desai, Yuankai Huo, Zhishun Wang, Ravi Bansal, Steven C. R. Williams, David Lythgoe, Fernando O. Zelaya and Bradley S. Peterson. Reduced perfusion in Broca’s area in developmental stuttering . Human Brain Mapping DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23487
Image: Blue regions represent areas of decreased blood flow in children and adults with stuttering when compared to fluent healthy participants. The red areas represent relatively higher blood flow. Credit: Children’s Hospital Los Angeles
Last Updated on December 11, 2023